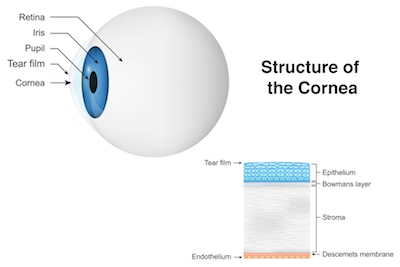
Keratoconus
A clinical condition characterised by thinning and forward protrusion of the cornea resulting in a conical shape. It usually affects both eyes and is found in patients of young age. Both genders are equally affected. The risk of inheritance is reasonably low.
Symptoms
Patients usually suffer from:
- Diminished vision
- Astigmatism (High Cylindrical number)
- Myopia
Causes
Etiology of Keratoconus is unclear; however, some factors may aggravate the condition, which include:
- Eye rubbing
- Hormonal variations
- Genetic predisposition
These factors lead to the cornea bulging forwards to form an irregular cone shape causing distortion of image
Treatment
- Spectacles
- Contact lens (Semisoft or RGP or Rose K contact Lenses)
- C3R or CXL (Collagen crosslinking) – The cornea is subjected to 30 mins of UV radiation which leads to cross linking of the corneal substance (collagen fibres) thereby increasing the physical strength of the cornea by upto 300%. Thus further progression of keratoconus can be arrested
- Intacs implants – Plastic implants are placed in the peripheral cornea, which helps flatten the central cornea, thereby improving the unaided vision. Patients are able to return back to normal glass- wear or comfortable contact lens wear post treatment. This procedure is painless and simple to perform.
- Surgical treatment: Corneal Transplant – In cases with advanced Keratoconus with very thin cornea, the cornea needs to be replaced with a donor cornea.
Occular Surface Disorders include
- Dry Eye Disease (DED)
- Corneal stem-cell deficiency
- Ocular allergic diseases
- Eyelid margin diseases such as Blepharitis and Meibomitis
- Ocular hyposensitivity and Neurotrophic Keratopathy
- Infections
- Conjunctivitis (red eye)
- Corneal ulcers
Symptoms
- Watering
- Heaviness in eyes
- Itching within the eye
- Diminished vision
- Pricking sensation within the eye
Dry eye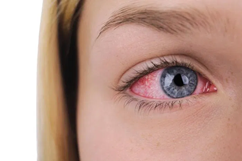
Dry eye is a very common disease which occurs due to lack of moisture in the eye or tears. Tears are considered essential for normal lubrication of eyes as well as to wash away foreign bodies and particles. Dry eye leads to many other problems like irritation and sometimes even scarring of eyes.
Symptoms
- Sandy or scratchy feeling
- Burning or stinging of eyes
- Excessive tearing/watering
- Stringy discharge
- Redness and burning/pain in eyes
- Foreign body sensation and intolerance to digital devices like computers & mobiles
Causes
- Lack of lubrication of the eye
- Inadequate blinking
- Prolonged use of contact lenses
- Certain local, systemic and hormonal disorders
- Low humidity/ Air conditioned environment
- Aging
- Smoking
- Autoimmune diseases
- Medications like decongestants and antihistamines
- Pollution/ dust/ smoke
- Excessive use of digital devices (Computer Vision Syndrome)
Treatment
- Lifestyle modification – Patients are advised to make a conscious effort to blink regularly and minimise their screen-time.
- Lubricating eye drops – Artificial tears eye drops is the principal treatment of dry eye.
- Lubricating eye ointments – Used sometimes at night for preventing eye dryness.
- Punctal plugs – These silicone microscopic plugs (inserted temporarily or permanently in the tear duct to block drainage) help conserve tears and prevent them from draining away. It is usually prescribed for patients who do not respond to frequent instillation of lubricants/eye drops.
Corneal Transplantation
Corneal Transplantation/ Grafting/ Keratoplasty is a surgical treatment used for removing some part or all damaged cornea. It is a transplant which is used for replacing damaged cornea with healthy- cornea tissues taken from the eyes of a suitable donor. Cornea transplant is used for improving eyesight, relieving pain as well as treating severe damage or infection. Keratoconus is one of the common reasons for using cornea transplant as under this eye disorder condition the cornea tends to change into a conical shape.
Indications for surgery
- Corneal scarring
- Corneal dystrophies
- Keratoconus
- Pseudophakic bullous keratopathy
- Infections (Corneal Ulcers)
Procedure
There are many methods of performing Corneal Transplant. Selection of the method of Corneal Transplant generally depends on which part of the cornea is damaged.
- DALK (Deep Anterior Lamellar Keratoplasty) – Reshaping or replacing middle and outer cornea.
- PK (Penetrating Keratoplasty) – full thickness Corneal Transplant
- DSAEK (Descemet Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty) / DMEK (Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty) / PDEK (Pre-Descemet Endothelial Keratoplasty) – Replacement of deeper parts of the cornea
Corneal transplant is usually carried out using local or general anaesthesia. Corneal Transplant/ Grafting is a day care surgery.
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis, sometimes also known as red eye is a condition which causes inflammation of the mucous membrane which lines the white part of the eye and the eyelid. It is caused due to viral or bacterial infection and chemicals, smoke and allergies. Both bacterial and viral types of conjunctivitis are contagious. People having conjunctivitis are always recommended to maintain hygiene and avoid close interactions with others.
Symptoms
- Redness
- Foreign- body sensation (feeling of something stuck in eye)
- Excessive tearing
- Burning or itching sensation in eye
- Glare – heightened sensitivity to light
Treatment
Treatment primarily consists of antibiotic drops for infectious/ bacterial conjunctivitis. Affected patients should always wash their hands thoroughly, avoid sharing towels or washcloths with others and should avoid touching their eyes. Eye-makeup should be avoided.
Corneal Ulcer/ Keratitis 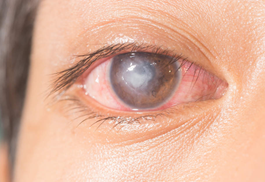
Corneal ulcer is an open sore or erosion involving the cornea.
Symptoms
- Hazy or blurry vision
- Watery and painful eyes
- Severe redness
- Pus like Discharge and itching
- Increased light sensitivity
- White patch on cornea
Causes
- Infection with viruses, parasite, fungi or bacteria
- Injury with a foreign object such as fingernail, vegetative matter, contact lenses
- Foreign bodies present in eye
- Severe dryness of eyes
- Scratches on eye surface
- Severe allergic- eye disease
- Several inflammatory disorders
Treatment
Evaluation: To know the cause of the corneal ulcer, specialists scrape the ulcer for evaluation of the causative microorganism and to initiate appropriate drug therapy
Treatment
- Antibiotic drops are given to the patients suffering from corneal ulcer caused by bacteria
- Severe corneal ulcers sometimes need surgical treatment (corneal transplant) – In case of failure of medical management through eye-drops, the surgical treatment ensures eye integrity and it is the mainstay of the treatment in case of impending perforation
Corneal Abrasion
A corneal abrasion is a scratch on the corneal surface.
Causes
- Accidental injury with a fingernail or any sharp and pointed object
Treatment
- Eyes can be pad and bandaged for a day or two
- Bandage contact lens helps in accelerating the healing process
- Topical medications like antibiotics and lubricating eye drops
Pterygium 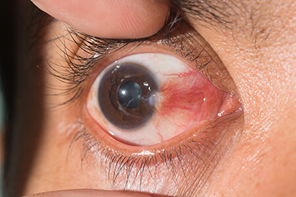
Pterygium is a non- cancerous growth which develops on the mucous membrane or conjunctiva which covers the white part of the eye. It is a non-cancerous or benign growth which is triangular shaped/ wedge shaped. It is common among people having exposure to wind and sunlight (UV light).
Symptoms
- Eye irritation, blurred vision and redness
- Itchiness or burning sensation
- Foreign body sensation in the eye
- White patch on the cornea
Causes
- Residents of hilly areas due to heightened UV exposure
- Exposure to sandy, dusty, sunny and windblown areas
Treatment
- For small Pterygium, topical use of eye-drops such as artificial tears, non-steroidal eye-drops or mild- steroid eye- drop are prescribed
- For progressing Pterygium / vision threatening Pterygium, surgical removal of the Pterygium is advised
- Surgical removal of the Pterygium is also carried out as a cosmetic procedure
FAQs for Corneal Transplant surgery
What are the risks of Corneal Transplant surgery?
There is a risk of the body rejecting the donor cornea that has been transplanted, and long term steroid therapy is required to prevent rejection. This predisposes the eye to steroid induced complications such as cataract and glaucoma.
How can we prevent corneal blindness?
Here are a few ways to prevent corneal blindness:
- Use clean water
- Treat Malnutrition e.g. Vitamin A deficiency
- Keep your surroundings clean and hygienic
- Avoid traditional medicine and home remedies for eye problems
What complication can arise from corneal disease?
Most corneal diseases and conditions can be managed with medical treatment. However, loss of sight is a potential complication of corneal diseases if not treated appropriately.
How can a corneal abrasion or corneal scarring be prevented?
The following precautions can prevent corneal abrasion:
- Blinking frequently
- Washing face with clean water
- In the case of a corneal foreign body, seek an expert’s opinion.
Do we need follow-up visits for corneal abrasion?
Yes, it’s best to visit your eye specialist for a check up to ensure your eyes are in good health. Do visit in case you feel any discomfort.
How is a child prone to corneal abrasion?
Here are some common ways in which your child can get a corneal abrasion:
- Injury with fingernails, toys, and other sharp and pointed objects like a pencil
- External irritants in the eye like dirt, pebbles, insects, wood shavings, hay, etc
- Exposure to chemical pollutants and fumes in the air
- In older children, ill-fitting lenses and improper use of make-up can also cause harm to their cornea
Are you a cornea transplant candidate?
Patients with conditions leading to corneal blindness benefit from corneal transplantation. Some of these indications are:
- Corneal scarring from past infections, injuries or surgeries
- Keratoconus and other conditions with thin and distorted cornea
- Swelling in cornea due to hereditary weakness of corneal cells or due to surgery
- Complications from LASIK, chemical injuries
Will my eye color change after corneal transplantation?
No it will not. There is a common misconception that a blue-eyed person’s eyes cannot be used for transplantation in a brown-eyed person. The only tissue used in the transplant is the cornea, which has nothing to do with the colored part of the eye.
Is the whole eye replaced during transplantation?
No it is not. The eyeball is connected to the brain by the optic nerve which is a part of the central nervous system, therefore the entire eye cannot be transplanted.
How is a cornea transplanted?
A cornea transplant happens under local anesthesia. General anesthesia is used for children and apprehensive or nervous patients. It’s a painless operation and takes about one hour to perform.
The diseased, cloudy, opaque cornea is removed from the patient’s eye using a special blade, and replaced by a new clear cornea from the donor’s (deceased person’s) eye. The new cornea is then sutured or stitched into place.
Recently, a new technology called Femtosecond Laser (IntraLaseTM) is available to make precise laser aided cuts in the donor and host cornea. Intralase-aided cuts improve wound healing and require less number of sutures leading to faster recovery.
How successful is corneal transplantation?
Corneal transplantation restores vision only in eyes that have been partially blinded by corneal disease. If a person has lost vision due to glaucoma, a detached retina, or degenerative change, and the retina has been damaged or destroyed, nothing can restore lost sight.
The success rate can vary from 90% (good final vision with glasses) to 10-20%, which is ascertained by evaluating each patient during the diagnosis.
The factors that impact the success rate are –
- Basic corneal disease (some types of corneal disease respond better to corneal transplantation than others)
- State of the donor’s cornea
- Surgical technique and skill
- Healing ability of the recipient cornea
- Sensitivity reactions between donor and recipient cornea may lead to transplant rejection
- Presence of concurrent eye diseases like glaucoma, retinal diseases reduce the chances of good visual outcome
The advantages of lamellar keratoplasty (newer techniques) are better visual outcome, quicker rehabilitation and lower rates of transplant rejection.
How does the vision change after corneal transplantation?
After a successful operation and if the graft is accepted by the patient’s eye (and rejection is ruled out), the vision starts to improve with time (provided the lens and retina are healthy and normal)
Healing after corneal transplant is a slow process and takes up to 1 year before all sutures can be removed. The vision fluctuates over the first 6 months and glasses are prescribed after healing is complete. Additional surgery like LASIK or PRK can be done if a patient wants to do away with glasses.
What is post operative care after corneal transplantation?
Patients will need one day of hospitalization and one month of rest at home, though they can get back to light work soon after. Over the following 6 months to one year, they should make frequent follow up visits to the doctor as suggested by him/her.
It is important to maintain good hygiene, avoid rigorous physical activity and not rub the operated eye.
If there is any pain, redness, watering, light sensitivity and decreased vision, even months or years after the surgery, consult your eye doctor immediately.
What is corneal graft rejection?
Any organ transplant carries a risk of rejection. The patient’s immune system can identify the transplanted cornea as a foreign body and reject it. A severe rejection episode can cause irreversible loss of function and graft fails. If early warning signs are recognized, and regular follow up visits are made, the risk of graft failure due to rejection can be prevented. Many factors like graft rejection, infection, astigmatism and glaucoma limit the success of corneal grafting. Despite such limitations, corneal transplant is still the most successful organ transplant procedure.
FAQ for Dry Eyes
What are some tips for managing dry eye disorder?
You can support dry eye syndrome treatment by following simple tips:
- Stay clear of the environment that may induce dry eyes. Avoid areas that might be abundant in dust, smoke, or wind.
- Use eye drops or ointments to ensure that your eyes stay lubricated.
- Blink frequently – People tend to blink much less while working on a computer, digital display devices, etc. The decreased rate aggravates mild dry eye symptoms. Make sure to perform a full blink in a way that you squeeze your eyelids together. This action spreads a fresh layer of tears over your eyes.
- Remove eye makeup thoroughly – Eyeliner, kohl, eye shadows, etc. clog the skin and meibomian glands under the eyelashes.
- Following eye care routine – Apply moist washcloth for at least three minutes to close eyelids. Gently wash them with a mild cleanser and moisturizer with eye care cream. You can also put warm compresses of cotton on your eyes to relax them.
- Wear quality sunglasses – Wind, dust, and other irritants in the air can worsen dry eye symptoms. That’s why it becomes vital to choose quality sunglasses while stepping outside. It would be best if you go for a wrap-style frame as it not only covers your eyes but gives full protection to the nearby areas too.
- Medicine adjustment – Several medicines can acutely cause dry eyes or worsen mild dry eye symptoms. Antidepressants, medicines for controlling blood pressure, etc. can exacerbate the situation. Consult your doctor and adjust the medication.
What are the kinds of dry eye surgery available?
Surgery is a rare treatment for Dry eye. However, there are different types of dry eye surgery that might involve blocking or closing tear ducts. Dry eye surgery can also be done to adjust the lower eyelid of the patient, so it is not loose. One of the treatment options is inserting punctal plugs in the patients tear ducts. The other type of surgery are:
- Thermal cautery: Thermal cautery is seen as a measure to treat dry eyes when punctal plugs fail to suit the patient. In this the surgeon uses a heated wire to shrink tissues around tear ducts. This permanently closes the duct and does not let tears drain, allowing them to be retained on the surface for longer.
- Salivary gland transplantation: Salivary gland transplantation is a type of dry eye surgery when your tear glands do not produce many tears. In this surgery, the surgeon may remove some parts of salivary glands from the patient’s lower lip and graft them to the upper eyelid.
What are the foods that may help me treat dry eye syndrome treatment?
Food rich in omega-3, omega-6 fatty acids, vitamin E, and vitamin A may help you in dry eye syndrome treatment.
Does smoking affect dry eyes?
Yes, when you smoke, dangerous elements get inside your bloodstream, thereby causing damage to your eyes. It increases the risk of getting cataracts, age-related macular degeneration, and dry eyes.
Is there any disease that can cause dry eyes?
Although dry eyes disorders are multifactorial, still some diseases can cause this eye condition, like:
● Rosacea
● Collagen vascular diseases
● Rheumatoid arthritis
● Congenital eye problem
What can be complications of dry eye syndrome treatment?
After dry eye syndrome treatment, people mostly have no long-term complications. Dry eyes sometimes cause conjunctivitis, which generally does not require treatment. But, if it is recurring, then it is a sign that you may need to talk to your specialist.
surgeries per year
patients per year
procedures per year
eye care specialists